|
|
|
|
This is Emy.
Emy receives many emails throughout the day.
Emy always reports suspicious emails.
Emy always checks if the domains' sender addresses and the domains' links are reliable.
Be smart.
Be like Emy.
|
|
|
|
Insight:
Phishing Emails - Vol. 2
|
As already explained in the first episode (Episode 1), Phishing is one of the main vehicles for cyberattacks.
It can take many forms. In the first episode, we focused on credential theft (Credential Harvesting). Today, we'll focus on the "classic" email scam. Here's an example:
|
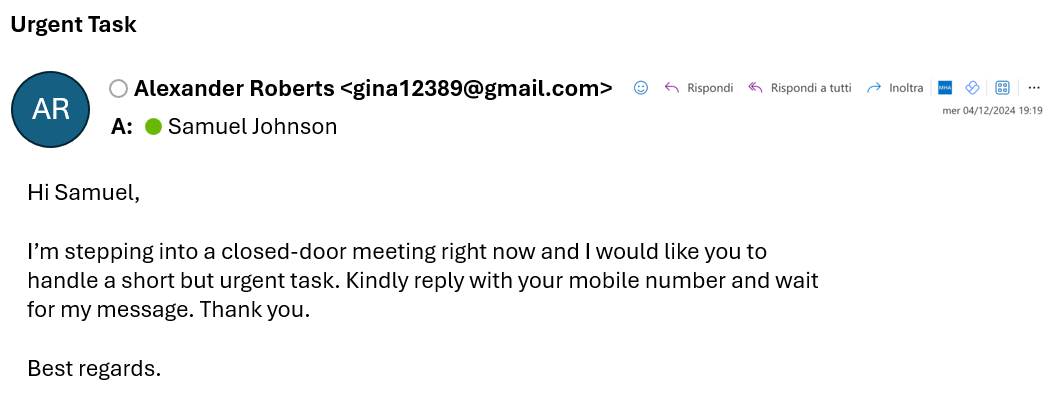
|
In this case, the attacker’s goal is to obtain the recipient’s phone number to establish direct contact with the victim. Typically, the sender will asks for gift cards (e.g., Amazon, Apple, etc.) to be purchased and sent via WhatsApp.
It is important to underline that cybersecurity is not solely the responsibility of the IT department but a commitment that involves all users. For this reason, here are some useful checks we recommend you perform when you recive an email:
Check the sender: in the example, the email address is associated with a generic Gmail account and the username does not match the displayed name (Alexander Roberts)
Verify the links: even though there are no links in this case, it’s always important to ensure that links in the email point to known and reliable domains.
Additionally, with the Christmas holidays approaching, we want to remember the importance of staying vigilant against online scams.
You might receive phishing emails with links redirecting to fake e-commerce sites. So, as previously mentioned, always verify domain names and make purchases only from official and known websites.
What should you do if in doubt?
Always REPORT suspicious emails.
Clicking on the button below will provide access to a detailed guide on how to report suspicious emails (we promise, it’s not a phishing link!).
Be smart
Be like Emy.
|
|
|
|
|
|